The respiratory system (or ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for the process of respiration in an organism. The respiratory system is involved in the intake and exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between an organism and the environment.
The human respiratory system is a series of organs responsible for taking in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide. In terrestrial animals, this is accomplished by breathing. The human body needs oxygen to sustain itself. A complete lack of oxygen is known as anoxia and a decrease in oxygen is known as hypoxia. After four to six minutes brain cells without oxygen brain cells are destroyed and an extended period of hypoxia leads to brain damage and ultimately death.
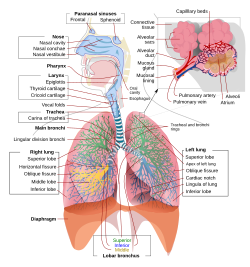
In air-breathing vertebrates, respiration takes place in the respiratory organs called lungs. The passage of air into and out of the lungs to supply the body with oxygen (and expel carbon dioxide) is called breathing. In humans and other mammals, the anatomical features of the respiratory system include include trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, lungs, and diaphragm. Molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide are passively exchanged, by diffusion, between the gaseous external environment and the blood. This exchange process occurs in the alveoli air sacs in the lungs.
In humans, the average rate of breathing is dependent upon age. Newborns up to 6 weeks take 30 to 60 breaths per minute, while the average resting respiratory rate for adults is 12 to 20 breaths per minute. Physical exertion also has an impact on respiratory rate and healthy adults can average 45 breaths per minute during strenuous exercise.
In fish and many invertebrates, respiration takes place through the gills. Other animals, such as insects, have respiratory systems with very simple anatomical features, and in amphibians even the skin plays a vital role in gas exchange. Plants also have respiratory systems but the directionality of gas exchange can be opposite to that in animals. The respiratory system in plants also includes anatomical features such as holes on the undersides of leaves known as stomata.
Post a Comment